The industrial sector represents a significant (30%) proportion of primary energy-related carbon emissions in the U.S - that’s 1,360 million metric tons of carbon dioxide, according to 2020 analysis from the U.S. Energy Information Administration.
Decarbonization measures have the potential to reduce these emissions through a combination of energy efficiency, industrial electrification, low-carbon energy sources, and carbon capture, utilization and storage (CCUS). Along the way, facilities can also benefit from decarbonization measures through improved equipment performance, increased productivity and operational cost savings.
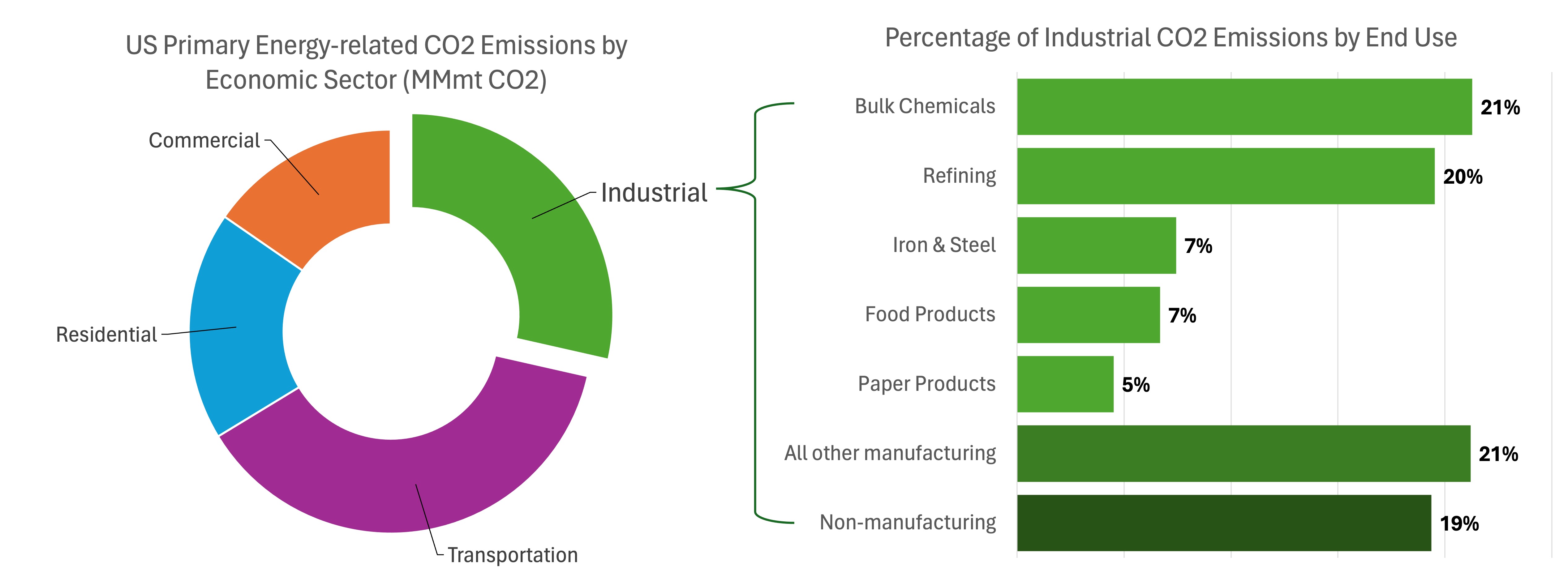
Breakdown of carbon dioxide emissions associated with U.S. industrial sector
Data source: “Annual Energy Outlook 2023 with Projections to 2050.” U.S. EIA, March 16, 2023.
Assessment Tools
To support facilities’ journeys towards decarbonization, a team of researchers at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (LBNL) and the University of California, Davis (UC Davis) have developed a set of online tools. Two tools - the Facility CO2e Flow Tool and the Levelized Cost of Avoided CO2e - are currently available for use, with two more planned for release in 2025.
These free tools are available for anyone, from students and faculty to consultants and companies, to use in techno-economic evaluation and prioritization of decarbonization measures.
This project is part of a collaborative effort on industrial decarbonization between researchers at LBNL and UC Davis. The tools were originally developed to support the technical assessments conducted by the U.S. Department of Energy Industrial Assessment Centers in line with the program’s growing emphasis on decarbonization and resiliency alongside efficiency and performance. For more information on Industrial Assessment Centers, visit the Department of Energy’s IAC webpage.
Tool #1: Facility CO2e Flow Tool (FCFT)
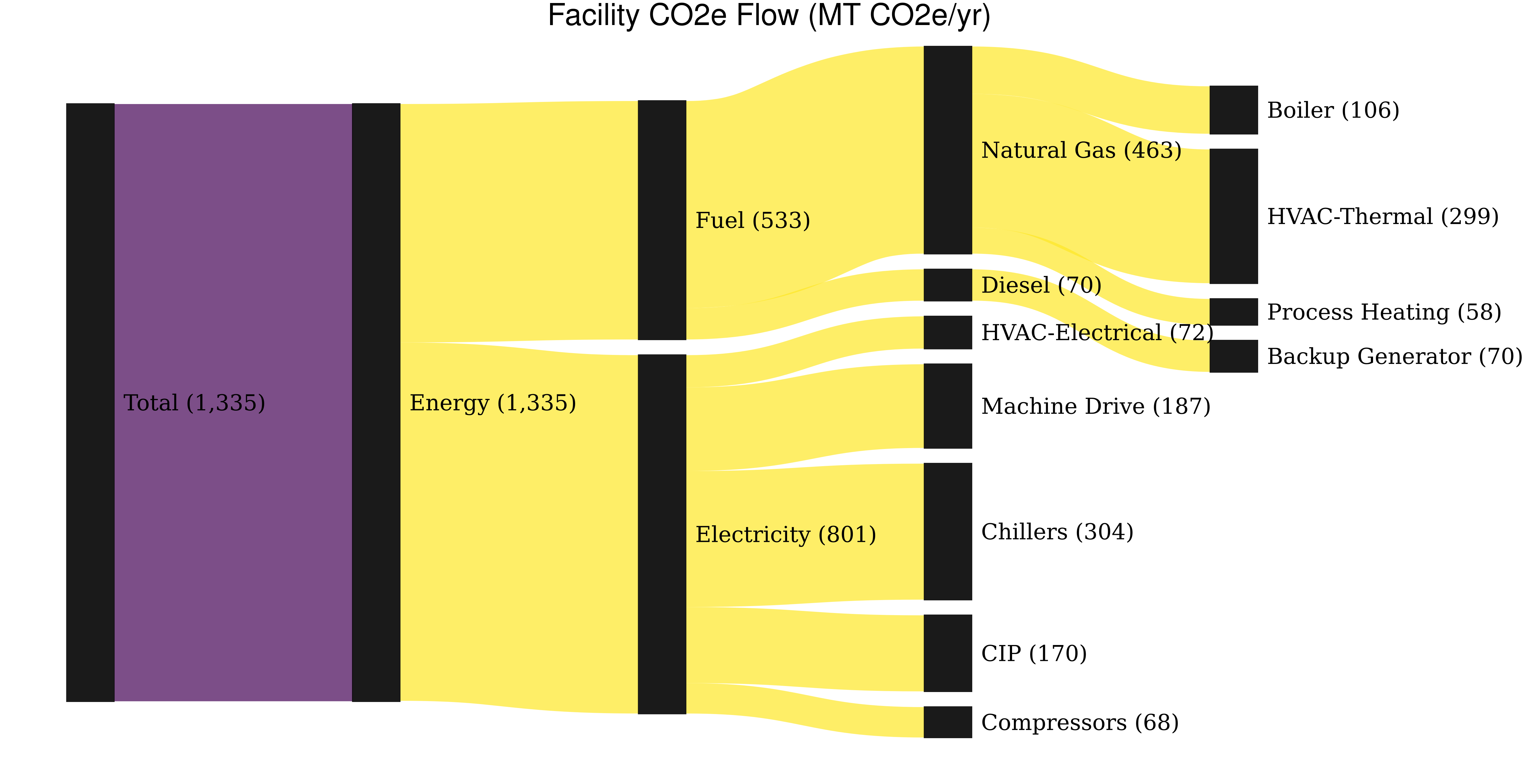
This tool takes a facility’s energy flows by process and visualizes the facility’s Scope 1 and 2 CO2e emissions using an interactive Sankey Diagram. This can help facilities identify and prioritize high emitting sources and hotspots, as well as other patterns and trends in their CO2e emissions. Download Source Code through Github
| Tool #2: Levelized Cost of Avoided CO2e (LCAC)LCAC is a levelized estimate of per unit cost of CO2e abatement based on the lifetime costs and savings associated with a suite of measures or a specific measure. This tool helps facilities calculate LCAC for each decarbonization measure and use this metric when analyzing potential decarbonization assessment recommendations. |
Meet the Team
This project is part of a joint effort between Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) and the UC Davis Energy and Efficiency Institute (UC Davis EEI). Visit their websites to find out more about the innovative energy-related work conducted by Berkeley Lab and UC Davis EEI.
| |
Prakash Rao Head of Building & Industrial Applications Department; Energy/Environmental Policy Research Scientist/Engineer |
Unique Karki Energy/Environmental Technology Researcher II |
 | |||
Kelly Kissock Faculty Director, Energy and Efficiency Institute; Professor, Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering |
Ovais Khan Master’s Student |
Muhammad Ali Qamar PhD Student |
Vedant Sinha Master’s Student |







